A. Online stability and interaction detection
Real timeDetect instabilities and interactions between elements.
Continuous assessment of stability and interactions in networks with high power-electronics penetration, enabling rapid mitigation.
The project embraces the digital and green transition to develop a High-Precision, High-Performance Computing-enabled Digital Twin (HP2C-DT) for modern power systems. HP2C-DT represents with high fidelity transmission, distribution, generation, railway and industrial networks, aiming to maximize resilience and real-time performance during the transition towards a 100% renewable system.
HP2C-DT is a digital twin concept for power systems that blends physics-based models with real-time data, exploiting central HPC and edge computing to enable high-speed autonomous decision-making. It supports network owners and operators to operate safely power-electronics-dominated systems during the energy transition.
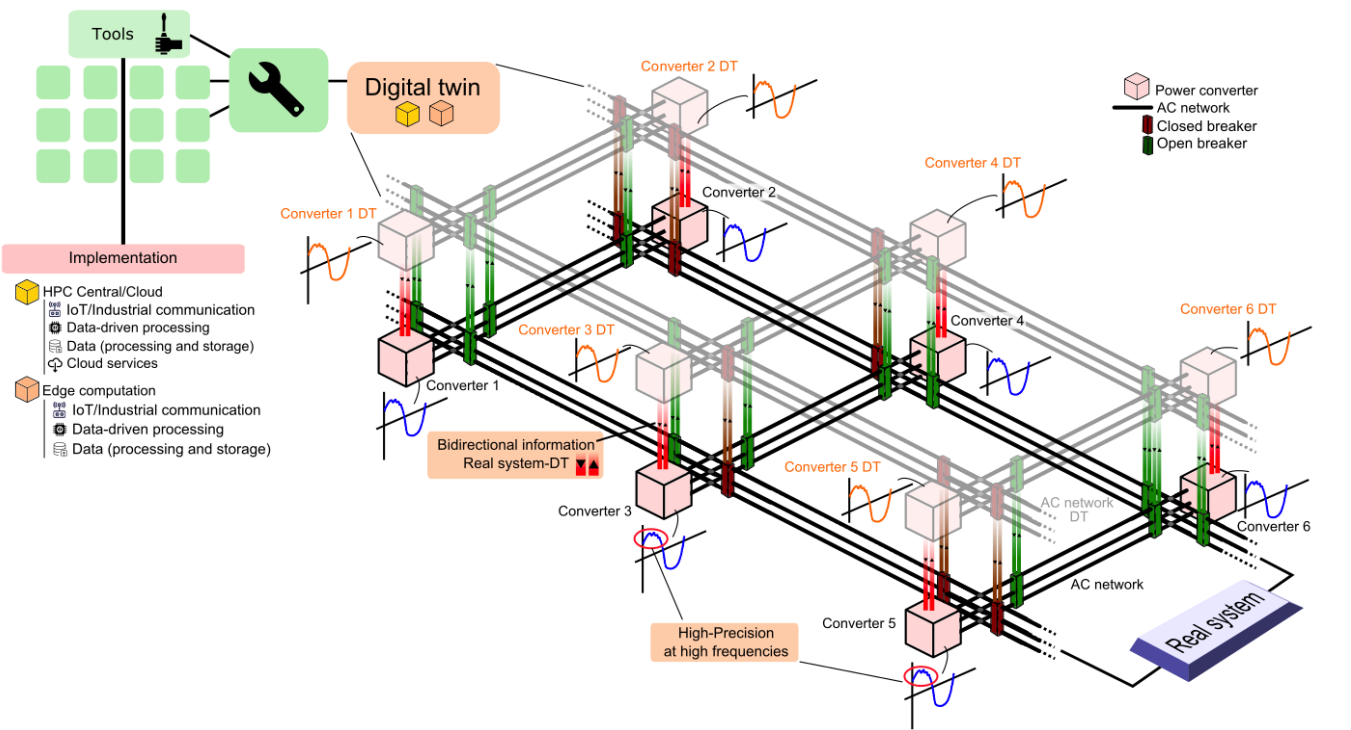
Figure: General structure of the HP2C-DT digital twin
Detect instabilities and interactions between elements.
Continuous assessment of stability and interactions in networks with high power-electronics penetration, enabling rapid mitigation.
Optimal operation and real-time equivalents calculation.
Optimizes operation leveraging power electronics controllability and computes equivalents (incl. short-circuit with PE) for system studies.
Protection tuning and coordination based on network state.
Adapts protections to topology, short-circuit capability and control mode (grid-following/forming), maximizing resilience.
Preventive multi-period analysis.
Generates and evaluates scenarios with combinations of contingencies (N-2) to support preventive decisions improving performance and resilience.
Automatic/autonomous grid operation.
Executes decisions based on tools A–D, distributing computation between central (or cloud) HPC and the edge for fast, coordinated responses.
Future Generation Computing Systems journal
This paper presents HP2C-DT, an HPC-enabled digital twin architecture that overcomes the trade-off between real-time responsiveness and computational demands, validated through a power grid use case with improved efficiency, scalability, and responsiveness.
Eigenverlag des Österreichischen Verbandes für Elektrotechnik
This article presents the development of a High-Performance Computing-enabled Digital Twin (HPC-DT) as an innovative solution designed to significantly enhance real-time power system management for grid operators. It begins by providing a comprehensive over-view of the HPC-DT architecture, detailing its key components and the technical methodology for integrating the digital twin with actual power systems. Following the architectural discus-sion, the article introduces a suite of specialized tools, many of which leverage the computa-tional power of HPC systems, to illustrate the practical capabilities of the proposed concept.
International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems
This paper presents a critical and practical approach to the evolution of distribution network reconfiguration algorithms, reviewing different methodologies, including classical heuristic algorithms, advanced meta-heuristic methodologies and purely mathematical approaches, analyzing their theoretical foundations, implementation strategies and computational complexity, based on extensive literature review and our own empirical testing.
IEEE Transactions on Power Systems
A contingencies probabilistic analysis in the IEEE 118-bus electrical model using a digital twin and contingencies simulations to estimate failure probabilities. BLA BLA
This work develops an adaptable distributed computing algorithm to optimize diverse functions efficiently. It is framed within a project that leverages high-performance computing and digital twins to enable sustainable and resilient modern power systems.
This thesis analyses consecutive contingencies in the IEEE 14-bus electrical model using a digital twin and MonteCarlo simulations to estimate failure probabilities. The methodology validates statistical models, identifies critical elements, and highlights the implications for grid resilience and future research.
This project presents Electra, a web based interactive viewer designed to visualize, edit, and analyse electrical networks directly from the browser. The tool combines an intuitive graphical interface with a validated computation engine to enable power flow studies, detailed inspection of grid components, and dynamic interaction with network models. The methodology integrates agile development, modular architecture, and standard data formats, offering an accessible and scalable environment aimed at improving teaching, research, and collaborative work in modern power system analysis.

Project Manager and Industrial Engineering teacher

HPC Software Research Area Director at BSC

Phd Candidate and data engineer.

Postdoctoral researcher. HPC and simulations.

Phd Candidate and power systems engineer.

Phd Candidate and Machine Learning Engineer.

Postdoctoral researcher. HPC and simulations

Support Research Assistant and Computer Science Teacher

Master's student and Industrial Engineering student.

Support Research Assistant

Master's student and Industrial Engineering student.

Bachelor's degree student in Informatics Engineering



Proyectos Estratégicos Orientados a la «Transición Ecológica y a la Transición Digital
2021
The Project TED2021-130351B-C21 (HP2C-DT) is funded by MICIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by the European Union NextGenerationEU/PRTR.
