A. Online stability and interaction detection
Real timeDetect instabilities and interactions between elements.
Continuous assessment of stability and interactions in networks with high power-electronics penetration, enabling rapid mitigation.
The project embraces the digital and green transition to develop a High-Precision, High-Performance Computing-enabled Digital Twin (HP2C-DT) for modern power systems. HP2C-DT represents with high fidelity transmission, distribution, generation, railway and industrial networks, aiming to maximize resilience and real-time performance during the transition towards a 100% renewable system.
HP2C-DT is a digital twin concept for power systems that blends physics-based models with real-time data, exploiting central HPC and edge computing to enable high-speed autonomous decision-making. It supports network owners and operators to operate safely power-electronics-dominated systems during the energy transition.
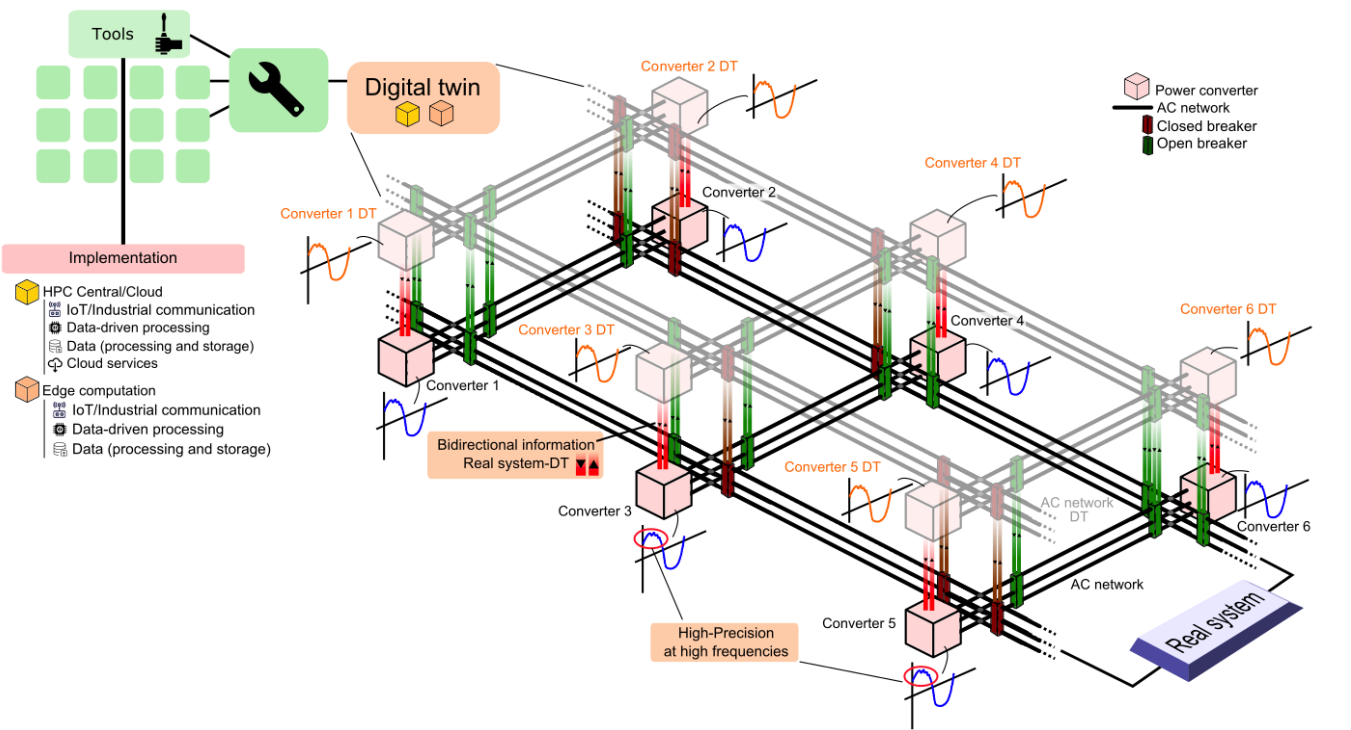
Figure: General structure of the HP2C-DT digital twin
Detect instabilities and interactions between elements.
Continuous assessment of stability and interactions in networks with high power-electronics penetration, enabling rapid mitigation.
Optimal operation and real-time equivalents calculation.
Optimizes operation leveraging power electronics controllability and computes equivalents (incl. short-circuit with PE) for system studies.
Protection tuning and coordination based on network state.
Adapts protections to topology, short-circuit capability and control mode (grid-following/forming), maximizing resilience.
Preventive multi-period analysis.
Generates and evaluates scenarios with combinations of contingencies (N-2) to support preventive decisions improving performance and resilience.
Automatic/autonomous grid operation.
Executes decisions based on tools A–D, distributing computation between central (or cloud) HPC and the edge for fast, coordinated responses.
The HP2C-DT coordinated project has developed a comprehensive Digital Twin of the electrical system supported by a distributed architecture that combines HPC, edge, and cloud computing in a coordinated manner. The HPC environment enables large-scale EMT simulations and high-fidelity dynamic models, the edge layer facilitates local processing close to the infrastructure, and the cloud/server layer acts as an integration point for data, models, and services.
This scalable architecture allows for accurate representation of modern electrical systems, incorporation of near real-time information, and execution of advanced analysis and optimization tools. The project has successfully integrated physics-based models with real-time data, enabling high-speed autonomous decision-making for power system operators.
Eigenverlag des Österreichischen Verbandes für Elektrotechnik
This article presents the development of a High-Performance Computing-enabled Digital Twin (HPC-DT) as an innovative solution designed to significantly enhance real-time power system management for grid operators. It begins by providing a comprehensive overview of the HPC-DT architecture, detailing its key components and the technical methodology for integrating the digital twin with actual power systems. Following the architectural discussion, the article introduces a suite of specialized tools, many of which leverage the computational power of HPC systems, to illustrate the practical capabilities of the proposed concept. The energy transition towards 100% renewable energy systems necessitates innovative tools to support power system operators in managing networks, particularly in light of the challenges posed by replacing conventional synchronous generation with power electronics (PE)-interfaced renewable energy systems.
Conference/Journal Publication
This paper investigates how grid-forming (GFM) and grid-following (GFL) control strategies in inverter-based resources (IBRs) influence line distance and differential protection in converter-dominated transmission systems. A modified IEEE 39-bus system is evaluated with GFM and GFL units equipped with low-voltage ride-through logic, current limiting, and positive- or negative-sequence prioritization. Distance protection is implemented with a mho characteristic, while line differential protection uses an alpha-plane approach. Results show that phase-to-ground loops in distance protection can substantially overestimate the fault location near the Zone-1 reach. For line differential protection, external faults may cause the operating point to briefly enter the trip region of the alpha-plane, even for the healthy-phase in ABG faults under GFL control and during the initial moments of the fault, demanding strong external security measures.
Conference/Journal Publication
As power systems rapidly transition to a landscape dominated by inverter-based resources (IBRs) with grid-forming (GFM) controls, existing protection philosophies face growing challenges. This paper presents a case study-based analysis of how distinct GFM control modes, dictated by grid codes, affect the reliability of conventional distance protection. A 14-bus, 400 kV network dominated by GFM IBRs was modeled in MATLAB/Simulink, incorporating four fault ride-through (FRT) strategies aligned with recent literature. Several distance protection strategies (self-, cross-, and memory-polarized Mho relays, as well as zero- and negative-sequence polarized quadrilateral characteristics) were assessed. The findings reveal that grid code requirements significantly influence the dependability and security of protection, with virtual-admittance and dual-sequence reactive current injection FRT strategies providing the most consistent performance. In particular, the zero-sequence polarized quadrilateral characteristic exhibited near-perfect dependability for faults involving ground across all evaluated IBR control modes.
Conference/Journal Publication
This paper focuses on applying data visualization and analysis techniques to explore and identify patterns in large datasets of power system operating points. The work addresses a database containing an extensive set of operating points of the power grid, randomly sampled within its feasible operating space, with system stability assessed for each point. The methodology includes data preprocessing, dimensionality reduction using PCA, t-SNE, and UMAP techniques, clustering methods (k-means and DBSCAN), and visualization to extract meaningful insights. The main objective is to determine which factors have the most relevant influence on grid stability, providing a solid foundation for future research directions or potential improvements in grid operation and management. The case study uses the NREL-118 system, consisting of 118 buses, 53 generators (including 18 converter-interfaced generators), operating under different control modes.
Conference/Journal Publication
This study proposes a tool embedded in a Digital Twin (DT) of the power system to identify potential undesirable interactions that may emerge within the system. The approach assumes that an up-to-date and accurate digital model of the power grid is available, but only black box models of the IBRs connected to the grid are accessible. The methodology consists of two stages: firstly, data-driven techniques are utilised to determine the equivalent impedance model of the electrical network and that of the IBR connected to that same bus. Then, the impedance models are employed to ascertain the stability of the system within the bandwidth permitted by these models. Equivalent models are obtained by running multiple EMT simulations in parallel within the DT. The Positive Mode Damping technique is used to determine interactions, based on the network's and converter's impedance models.
IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 135913-135928, 2024
This paper proposes an approach that leverages the inclusion of physical constraints into the loss function using a penalty factor and the utilization of bounds of optimization variables in the activation functions to enhance the generalization performance of tuned neural networks. The results indicate that this method significantly improves the success rate and computational speed gains of AC-optimal power flow (AC-OPF) calculations, especially when forward predictions are employed as warm-start points. The PINN models are trained using accurate AC-OPF solutions from slow high-precision interior-point solvers across several power system scenarios. The proposed PINN model offers a promising solution for adapting neural networks to diverse scenarios of a physical problem and provides a robust methodology for successfully addressing optimal power flow (OPF) problems in power systems.
Journal Publication
This paper analyses frequency dynamics in modern power systems with a high penetration of converter-based generation. A fundamental analysis of the frequency dynamics is performed to identify the limitations and challenges when the converter penetration is increased. The voltage-source behaviour is found as an essential characteristic of converters to improve the initial frequency derivative of Synchronous Generators (SGs). A detailed small-signal analysis, based on the system's eigenvalues, participation factors and mode shapes, is then performed in a reduced system for different converter penetrations, showing that the flexibility of grid-forming (GFOR) converters as well as the system's inertia reduction may lead to have a more controllable system frequency. First-order frequency responses can be programmed for high converter penetrations, when GFOR operation can impose their dominance over SGs. These results have been validated in the IEEE 118-bus system simulated in PSCAD.
Journal Publication
The increasing penetration of inverter-based resources (IBRs) is fundamentally reshaping power system dynamics and creating new challenges for stability assessment. Data-driven approaches, and in particular machine learning models, require large and representative datasets that capture how system stability varies across a wide range of operating conditions and control settings. This paper presents an open-source, high-performance computing framework for the systematic generation of such datasets. The proposed tool defines a scalable operating space for large-scale power systems, explores it through an adaptive sampling strategy guided by sensitivity analysis, and performs small-signal stability assessments to populate a high-information-content dataset. The framework efficiently targets regions near the stability margin while maintaining broad coverage of feasible operating conditions. The workflow is fully implemented in Python and designed for parallel execution. The resulting tool enables the creation of high-quality datasets that support data-driven stability studies in modern power systems with high IBR penetration.
Journal Publication
This study proposes a control strategy to ensure the safe operation of modern power systems with high penetration of inverter-based resources (IBRs) within an optimal operation framework. The objective is to obtain operating points that satisfy the optimality conditions of a predefined problem while guaranteeing small-signal stability. The methodology consists of two stages. First, an offline analysis of a set of operating points is performed to derive a data-driven regression-based expression that captures a damping-based stability index as a function of the operating conditions. Second, an Online Feedback Optimization (OFO) controller is employed to drive the system toward an optimal operating point while maintaining a secure distance from the instability region. The proposed strategy is evaluated on an academic test case based on a modified version of the IEEE 9-bus system, in which synchronous generators are replaced by IBRs operating under both grid-following and grid-forming control modes. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method and are discussed in detail.
Journal Publication
Modern power networks face increasing vulnerability to cascading failures due to high complexity and the growing penetration of intermittent resources, necessitating rigorous security assessment beyond the conventional N-1 criterion. Current approaches often struggle to achieve the computational tractability required for exhaustive N-2 contingency analysis integrated with complex stability evaluations like small-signal stability. Addressing this computational bottleneck and the limitations of deterministic screening, this paper presents a scalable methodology for the vulnerability assessment of modern power networks, integrating N-2 contingency analysis with small-signal stability evaluation. To prioritize critical components, we propose a probabilistic Risk Index (Ri) that weights the deterministic severity of a contingency (including optimal power flow divergence, islanding, and oscillatory instability) by the failure frequency of the involved elements based on reliability data. The proposed framework is implemented using High-Performance Computing (HPC) techniques through the PyCOMPSs parallel programming library, orchestrating optimal power flow simulations (VeraGrid) and small-signal analysis (STAMP) to enable the exhaustive exploration of massive contingency sets. The methodology is validated on the IEEE 118-bus test system, processing more than 57000 scenarios to identify components prone to triggering cascading failures. Results demonstrate that the risk-based approach effectively isolates critical assets that deterministic N-1 criteria often overlook.
Journal Publication
This paper presents a critical and practical approach to the evolution of distribution network reconfiguration algorithms, tracing their development from foundational heuristic methods introduced in 1975 to contemporary state-of-the-art techniques. The article systematically reviews seven different methodologies, including classical heuristic algorithms (Merlin, Baran, and others), advanced meta-heuristic methodologies (particle swarm optimization (PSO) and genetic algorithms), and purely mathematical approaches (MILP-based), analyzing their theoretical foundations, implementation strategies, computational complexity, and performance metrics based on extensive literature review and our own empirical testing. Each methodology is assessed through standardized test systems, considering multiple objectives such as power loss minimization and voltage profile improvement. The comparative analysis reveals the strengths and limitations of each approach under various network conditions and operational constraints. Furthermore, this work provides significant value to the research community by offering an open-source repository containing documented implementations of all reviewed algorithms. This resource facilitates accessibility for newcomers to the field, promotes reproducible research, and accelerates the development of next-generation distribution network optimization solutions. The repository includes comprehensive documentation, test cases, and performance benchmarks.
Conference/Journal Publication
Digital twins are emerging as transformative tools for High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission systems, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and operational optimization. However, the effectiveness of these virtual replicas fundamentally depends on seamless, reliable data exchange with their physical counterparts and any other support system. The current landscape of HVDC digital twin implementations reveals a critical challenge: the absence of standardized data exchange protocols leads to vendor lock-in, interoperability issues between data provided by different vendors, and increased lifecycle costs. This paper argues for the adoption of standardized data exchange methodologies in HVDC digital twins and examines the suitability of the Common Information Model (CIM) defined in IEC 61970 as a foundation for this standardization, an established and proven data structure for electrical systems that also includes HVDC elements.
Future Generation Computing Systems journal
Digital twins are transforming the way we monitor, analyze, and control physical systems, but designing architectures that balance real-time responsiveness with heavy computational demands remains a challenge. Cloud-based solutions often struggle with latency and resource constraints, while edge-based approaches lack the processing power for complex simulations and data-driven optimizations. To address this problem, we propose the High-Precision High-Performance Computer-enabled Digital Twin (HP2C-DT) reference architecture, which integrates High-Performance Computing (HPC) into the computing continuum. Unlike traditional setups that use HPC only for offline simulations, HP2C-DT makes it an active part of digital twin workflows, dynamically assigning tasks to edge, cloud, or HPC resources based on urgency and computational needs. Furthermore, to bridge the gap between theory and practice, we introduce the HP2C-DT framework, a working implementation that uses COMPSs for seamless workload distribution across diverse infrastructures. We test it in a power grid use case, showing how it reduces communication bandwidth by an order of magnitude through edge-side data aggregation, improves response times by up to 2x via dynamic offloading, and maintains near-ideal strong scaling for compute-intensive workflows across a practical range of resources. These results demonstrate how an HPC-driven approach can push digital twins beyond their current limitations, making them smarter, faster, and more capable of handling real-world complexity.
The HP2C-DT project has developed and contributed to several open-source tools and resources that are available to the research community. These resources facilitate reproducible research and accelerate the development of next-generation power system solutions.
High-performance computing framework for systematic dataset generation
Open-source Python framework for generating large and representative datasets for stability assessment in power systems with high penetration of inverter-based resources. Includes adaptive sampling strategies and parallel execution capabilities.
Open-source repository with documented implementations
Comprehensive open-source repository containing documented implementations of distribution network reconfiguration algorithms, including classical heuristic methods, meta-heuristic approaches, and mathematical optimization techniques.
AC-OPF solver integration
Integration of AC Optimal Power Flow (AC-OPF) solver capabilities into the GridCal framework, enhancing its optimization capabilities for power system analysis.
Distributed computing framework implementation
Working implementation of the HP2C-DT framework using COMPSs for seamless workload distribution across diverse infrastructures, enabling dynamic task assignment to edge, cloud, or HPC resources.
This work develops an adaptable distributed computing algorithm to optimize diverse functions efficiently. It is framed within a project that leverages high-performance computing and digital twins to enable sustainable and resilient modern power systems.
This thesis analyses consecutive contingencies in the IEEE 14-bus electrical model using a digital twin and MonteCarlo simulations to estimate failure probabilities. The methodology validates statistical models, identifies critical elements, and highlights the implications for grid resilience and future research.
This project presents Electra, a web based interactive viewer designed to visualize, edit, and analyse electrical networks directly from the browser. The tool combines an intuitive graphical interface with a validated computation engine to enable power flow studies, detailed inspection of grid components, and dynamic interaction with network models. The methodology integrates agile development, modular architecture, and standard data formats, offering an accessible and scalable environment aimed at improving teaching, research, and collaborative work in modern power system analysis.
This master's thesis focuses on the development and implementation of digital twins for power grids, with particular emphasis on communication systems and practical implementation aspects.
This master's thesis addresses load forecasting in distribution networks using real-time measurements to improve prediction accuracy and grid management.
This directed work focuses on identifying critical eigenvalues in power systems through clustering techniques, enabling better understanding of system stability characteristics.
This master's thesis focuses on integrating an AC Optimal Power Flow (AC-OPF) solver into the GridCal framework, enhancing its capabilities for power system optimization.
This project develops a generalized approach for AC/DC power flow analysis, enabling comprehensive analysis of hybrid AC/DC power systems.
This project focuses on post-processing techniques for stability data analysis in electrical networks, enabling better interpretation and visualization of stability assessment results.
This work presents a comparative analysis of phasor calculation techniques for Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs), evaluating different methodologies for accurate phasor estimation in power systems.
The HP2C-DT project has made significant contributions to the advancement of knowledge in digital twin technologies for power systems. The project has developed novel methodologies for integrating high-performance computing into real-time digital twin workflows, addressing critical challenges in modern power systems with high penetration of inverter-based resources.
Key scientific contributions include the development of distributed computing architectures that seamlessly integrate HPC, edge, and cloud computing, enabling high-precision simulations and real-time decision-making. The project has also advanced the state-of-the-art in stability assessment, protection coordination, and optimization techniques for power-electronics-dominated networks.
The project addresses critical needs in the energy transition towards 100% renewable systems. By providing tools and methodologies for safe operation of power-electronics-dominated networks, HP2C-DT supports grid operators and network owners in managing the increasing complexity of modern power systems.
The open-source nature of many project deliverables facilitates knowledge transfer to industry and academia, promoting reproducible research and accelerating the adoption of digital twin technologies in the power sector. The project's contributions to stability assessment and protection coordination directly support the reliability and resilience of electrical networks during the energy transition.
The HP2C-DT framework and tools have potential applications in:

Project Manager and Industrial Engineering teacher

Principal Investigator (IP2)

HPC Software Research Area Director at BSC

Phd Candidate and data engineer.

Postdoctoral researcher. HPC and simulations.

Phd Candidate and power systems engineer.

Phd Candidate and Machine Learning Engineer.

Postdoctoral researcher. HPC and simulations

Support Research Assistant and Computer Science Teacher

Master's student and Industrial Engineering student.

Support Research Assistant

Master's student and Industrial Engineering student.

Bachelor's degree student in Informatics Engineering

Master's student

Master's student

Student

Student

Student

Researcher and Lecturer

Research Team Member

Research Team Member



Proyectos Estratégicos Orientados a la «Transición Ecológica y a la Transición Digital»
2021
The coordinated project HP2C-DT consists of two subprojects:
The Project TED2021-130351B-C21 (HP2C-DT) is funded by MICIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by the European Union NextGenerationEU/PRTR.
